In the world of technology, the versatility and power of Single Board Computers (SBCs) have made them indispensable tools for hobbyists, educators, and professionals alike. Whether you are building a DIY project, developing an IoT device, or setting up an industrial control system, choosing the right SBC can make all the difference. This guide will walk you through the essentials of what SBCs are, how to choose the right one for your needs, and why Geniatech stands out as a top choice in this field.
What Are Single Board Computers?
Single Board Computers (SBCs) are compact, fully functional computing devices that integrate all the components of a traditional computer onto a single circuit board. Unlike traditional desktop or laptop computers, which typically consist of a motherboard, separate processors, memory modules, and other peripheral components housed within a case, SBCs combine all these elements into a single, cohesive unit. This compact design makes SBCs an ideal choice for a wide range of applications, from educational purposes to embedded systems in industrial and commercial settings.
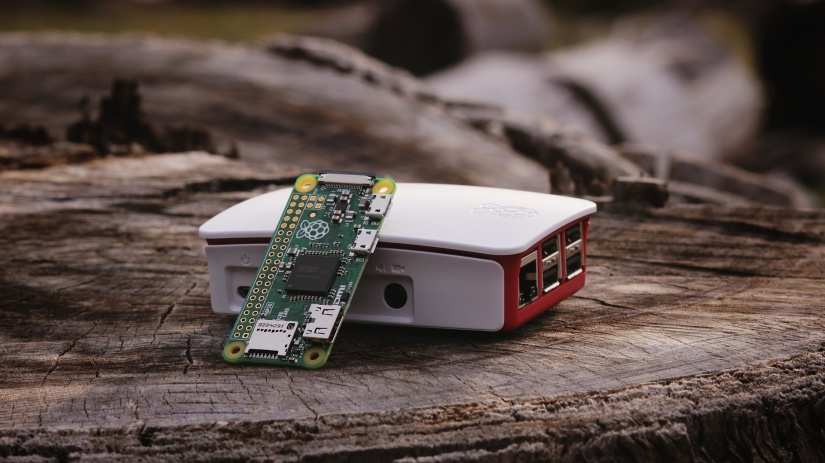

Basics of SBCs
- Processor (CPU): The central processing unit (CPU) is the brain of the SBC, responsible for executing instructions and processing data. SBCs often use energy-efficient ARM processors, though some models feature x86 processors.
- Memory (RAM): Random Access Memory (RAM) provides temporary storage for data that the CPU needs quick access to. The amount of RAM in an SBC can vary, typically ranging from 512MB to 8GB or more.
- Storage: SBCs include storage solutions for the operating system and data. This can be in the form of onboard flash storage, microSD card slots, or support for external storage devices.
- Input/Output (I/O) Ports: SBCs are equipped with various I/O ports, such as USB, HDMI, Ethernet, and GPIO (General-Purpose Input/Output) pins. These ports allow the SBC to interface with peripherals, networks, and other devices.
- Power Supply: SBCs can be powered through various means, commonly via a micro-USB or USB-C port, making them versatile and easy to deploy in different environments.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): Some SBCs come with integrated GPUs to handle graphics-intensive tasks, such as video playback or gaming.
Advantages of Single Board Computers
- Compact Size: The small form factor of SBCs makes them suitable for applications where space is limited, such as embedded systems and portable devices.
- Low Power Consumption: SBCs are designed to be energy-efficient, making them ideal for battery-powered projects and reducing operating costs in continuous-use scenarios.
- Cost-Effective: Generally, SBCs are more affordable than traditional computers, making them accessible for educational purposes, hobbyists, and prototyping.
- Versatility: SBCs can run various operating systems, including Linux, Android, and Windows IoT, making them adaptable to different use cases and development environments.
- Community and Support: Many popular SBCs have large communities of users and developers, providing a wealth of resources, tutorials, and support that can be invaluable for both beginners and advanced users.
Common Applications of SBCs
- Education: SBCs are widely used in educational settings to teach computer science, programming, and electronics.
- Home Automation: They can serve as the brains behind smart home systems, controlling lighting, security, and other IoT devices.
- Media Centers: With their ability to handle multimedia content, SBCs are often used to build custom home theater PCs (HTPCs).
- Industrial Automation: In industrial environments, SBCs can monitor and control machinery, manage data collection, and more.
- Prototyping and Development: Their affordability and versatility make SBCs perfect for developing and testing new software and hardware projects.
Single Board Computers have revolutionized the way we think about computing and development, providing powerful, flexible, and affordable solutions for a myriad of applications. Whether you’re a hobbyist looking to tinker with new projects or an industry professional developing cutting-edge technology, SBCs offer a robust platform to bring your ideas to life.
How to Choose the Single Board Computer
Choosing a single board computer (SBC) depends on several factors based on your specific needs and applications. Here are some key considerations to help you make an informed decision:
1. Purpose and Use Case
- Project Requirements: Determine the primary use case of the SBC (e.g., media center, IoT project, robotics, AI development, server, etc.).
- Processing Power: Assess the computational requirements. Simple tasks may need a less powerful SBC, while complex applications like AI or machine learning may require more powerful CPUs and GPUs.
2. Hardware Specifications
- CPU and GPU: Look at the processor type (ARM, x86, etc.) and clock speed. Consider a powerful GPU if you plan to handle graphics-intensive tasks.
- RAM: Ensure the board has sufficient memory for your applications. 1GB might be enough for basic tasks, but more demanding applications may require 4GB or more.
- Storage: Check for onboard storage options and expandable storage through SD cards or eMMC modules.
- Connectivity: Consider the number and type of USB ports, HDMI output, Ethernet ports, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and GPIO pins for interfacing with other devices.
3. Compatibility and Software Support
- Operating Systems: Ensure the SBC supports your preferred operating system (e.g., Linux, Android, Windows IoT).
- Community and Documentation: A strong community and good documentation can be invaluable for troubleshooting and getting the most out of your SBC.
- Driver Support: Check for compatibility with peripherals and available drivers.
4. Power Consumption and Thermal Management
- Power Requirements: Consider the power needs and how you will supply it (e.g., via USB, battery, or power adapter).
- Heat Dissipation: Look at the cooling solutions available, such as heat sinks and fans, especially if the board will be used in a high-performance or enclosed environment.
5. Size and Form Factor
- Physical Dimensions: Make sure the SBC fits within the physical constraints of your project.
- Mounting Options: Consider how you will mount or enclose the SBC in your project.
6. Budget
- Cost: Determine your budget and find an SBC that offers the best balance of features and performance within your price range.
- Additional Costs: Factor in costs for accessories, power supplies, cases, and storage.
7. Future Proofing
- Upgradeability: Consider whether the SBC can be upgraded in terms of hardware or software to meet future needs.
Popular Single Board Computers in the Market
Here are some popular SBCs to consider:
- Raspberry Pi: Widely used with strong community support, good for general purposes.
- NVIDIA Jetson Nano: Great for AI and machine learning projects.
- Geniatech SBCs: Combines AI with embedded applications, suitable for demanding projects.
- BeagleBone Black: Suitable for industrial applications and projects requiring real-time processing.
- ODROID: Known for higher performance in terms of CPU and GPU capabilities.
By evaluating these factors and matching them with your project requirements, you can choose the right single board computer for your needs. If you have a specific project in mind, I can help narrow down the options further.

Why Consider Geniatech as a Great Option
Geniatech is a well-known manufacturer of embedded systems and single board computers, particularly recognized for their integration of AI and computer vision capabilities. Here are some concrete advantages of choosing Geniatech products.
1. AI and Computer Vision Integration
- Embedded AI Capabilities: Geniatech SBCs often come with built-in AI processing capabilities, such as support for neural networks and machine learning models. This makes them ideal for applications in computer vision, edge AI, and IoT.
- Hardware Acceleration: Their boards frequently include hardware accelerators for AI workloads, like NPUs or dedicated AI chips, which significantly improve performance for AI applications.
2. Robust Performance
- High Processing Power: Geniatech SBCs are equipped with powerful processors (ARM-based, x86, etc.) that cater to demanding applications, providing strong computational performance.
- Memory and Storage: These boards typically offer ample RAM and storage options, which are crucial for data-intensive applications.
3. Connectivity and Expandability
- Versatile I/O Options: Geniatech boards provide a wide range of I/O interfaces including USB, HDMI, Ethernet, and GPIO, making them suitable for various interfacing and connectivity needs.
- Expansion Modules: They offer various expansion modules that can be added to the base SBC to extend functionality, such as additional sensors, communication modules, or custom interfaces.
4. Software Support
- Wide OS Compatibility: Geniatech SBCs support multiple operating systems including Android, Linux, and Windows IoT, providing flexibility depending on the project requirements.
- SDKs and Development Tools: They provide robust software development kits (SDKs) and tools that help developers to efficiently build and deploy applications.
5. Industrial-Grade Reliability
- Durability: Geniatech products are designed to be robust and reliable, suitable for industrial and commercial applications where long-term stability is essential.
- Quality Components: They use high-quality components to ensure the longevity and reliability of their devices.
6. Comprehensive Solutions
- End-to-End Solutions: Beyond individual boards, Geniatech offers complete solutions including hardware, software, and services that can accelerate development and deployment of IoT and AI projects.
- Customization Services: They provide customization services to tailor their products to specific project needs, which can be crucial for specialized industrial applications.
7. Strong Support and Community
- Technical Support: Geniatech provides strong technical support, helping customers troubleshoot issues and optimize their applications.
- Active Community: They have an active user community and extensive documentation, which can be very helpful for both beginners and experienced developers.
These advantages make Geniatech a strong contender for projects requiring robust, reliable, and high-performance embedded systems with a focus on AI and computer vision. If you have specific use cases or requirements, I can provide more targeted information on how Geniatech products might meet those needs.
Conclusion
Choosing the right Single Board Computer for your project is crucial to its success. By understanding your project’s requirements, evaluating the hardware and software capabilities of potential SBCs, and considering factors like connectivity, power consumption, and budget, you can make an informed decision. Geniatech stands out as a top choice due to its robust performance, AI and computer vision integration, industrial-grade reliability, and comprehensive support. Whether you are a hobbyist, educator, or professional, Geniatech’s SBCs offer a powerful and versatile platform to bring your ideas to life.

