Fanless computers, designed without traditional cooling fans, are becoming increasingly popular in industrial applications due to their durability and silent operation. This blog explores how fanless computers work, their benefits, and their various industrial uses. We’ll dive into their cooling mechanisms, compare active and passive cooling, and highlight why fanless computers are the go-to choice for many industries.
What Are Fanless Computers?
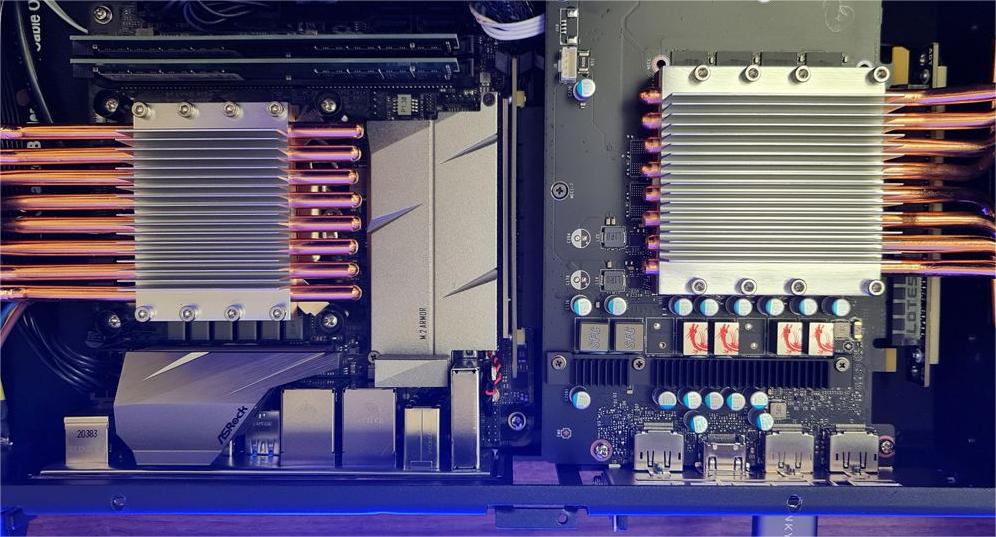
Fanless computers are a type of computing device designed to operate without traditional cooling fans. Instead, they use passive cooling methods to manage heat, making them silent and more durable than their fan-cooled counterparts. This design choice makes them ideal for environments where noise reduction and reliability are paramount.
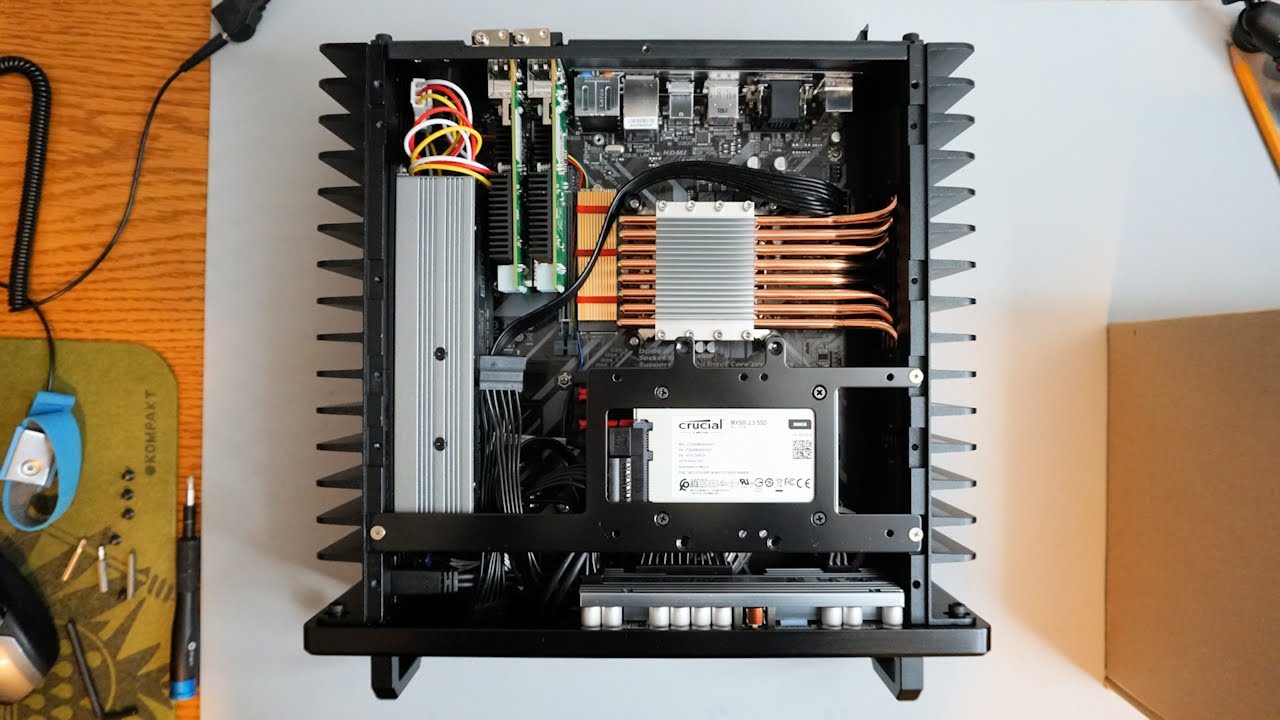

Core Components and Design Features
- Heat Sinks: Large metal components, typically made of aluminum or copper, that absorb and disperse heat away from critical components like the CPU and GPU.
- Thermal Pads and Pipes: These elements conduct heat from the processor to the heat sinks, ensuring efficient heat transfer and distribution.
- Efficient Component Layout: Components are strategically placed to maximize airflow and heat dissipation, even in the absence of active cooling systems. This thoughtful design minimizes hot spots and ensures consistent performance.
How Fanless Cooling Works
Fanless computers are designed to operate silently by using passive cooling methods instead of traditional fans. Here’s how they manage to keep cool and maintain performance without making a sound.
Fanless cooling relies on a few key components working together to dissipate heat effectively:
Heat Sinks
- Heat sinks are metal components, often made of aluminum or copper, that absorb heat from critical parts like the CPU and GPU.
- By having a large surface area, heat sinks spread out the heat, making it easier for the heat to dissipate into the surrounding air. Their efficiency in dispersing heat helps keep the internal temperature down.
Thermal Pads and Pipes
- Thermal pads are placed directly on heat-generating components to facilitate heat transfer, while thermal pipes (also known as heat pipes) conduct heat away from these components to the heat sinks.
- Thermal pads and pipes act as conduits, ensuring a continuous flow of heat away from critical parts. This efficient transfer of heat helps in maintaining stable temperatures across the device.
Efficient Component Placement
- The internal layout of a fanless computer is designed to maximize natural airflow and minimize heat build-up by strategically placing components.
- Proper placement of components allows for natural convection currents to form, where cooler air moves in to replace the warmer air being displaced by the heat sinks. This natural airflow aids in cooling without the need for active fans.
Maintaining Optimal Temperatures
By combining these passive cooling mechanisms, fanless computers achieve a balance between silent operation and effective thermal management. The heat sinks and thermal pipes work together to disperse heat efficiently, while the strategic placement of components maximizes airflow. This integrated approach ensures that fanless computers remain cool and reliable, even in environments where noise reduction is critical.
Understanding how these systems work together highlights the innovation behind fanless computers, making them an excellent choice for industrial applications where durability and silence are key.
Advantages of Fanless Computers in Industrial Settings
Fanless computers offer several distinct advantages that make them particularly well-suited for industrial environments. These benefits enhance their performance, longevity, and cost-effectiveness in demanding settings.
Silent Operation
Fanless computers operate silently, making them ideal for use in environments where noise reduction is crucial. This includes places like recording studios, offices, and medical facilities, where maintaining a quiet atmosphere is essential for productivity and comfort.
Durability and Reliability
Fanless computers are built to endure tough industrial conditions. Without fans to attract dust and debris, they are better suited to environments with high levels of dust, moisture, and extreme temperatures. This robustness ensures consistent performance and reduces the risk of damage over time.
Low Maintenance
The absence of fans and other moving parts significantly lowers the maintenance requirements for fanless computers. With fewer components that can wear out or fail, these systems have a longer operational lifespan and reduce downtime due to repairs.
Energy Efficiency
Fanless computers typically consume less power than their fan-cooled counterparts. This energy efficiency translates to lower operational costs, making them a cost-effective solution for industries looking to reduce their energy consumption and carbon footprint.
By offering silent operation, enhanced durability, minimal maintenance, and superior energy efficiency, fanless computers provide significant advantages in industrial settings. These benefits make them an attractive option for businesses aiming to improve reliability and reduce costs in challenging environments.
Active Cooling vs. Passive Cooling
When it comes to cooling computer systems, two primary methods are used: active cooling and passive cooling. Each has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different applications. Understanding these differences can help in choosing the right cooling solution for your needs.
What is Active Cooling?
Active cooling involves the use of mechanical components, such as fans and liquid cooling systems, to actively remove heat from the computer’s components. These systems work by forcing air or liquid over the heat-generating parts, rapidly dissipating heat to maintain optimal operating temperatures. Active cooling is highly effective, especially for high-performance systems, but it comes with certain trade-offs like noise and higher energy consumption.
Comparison Table: Active Cooling vs. Passive Cooling
| Feature | Active Cooling | Passive Cooling |
| Cooling Mechanism | Uses fans, liquid cooling systems, or other active components to dissipate heat. | Utilizes heat sinks, thermal pads, and efficient component layout to dissipate heat without moving parts. |
| Noise Level | Generates noise due to moving parts like fans. | Silent operation with no moving parts. |
| Cooling Efficiency | High efficiency; can handle high-performance components and heavy workloads. | Lower efficiency compared to active cooling; best for low to moderate workloads. |
| Energy Consumption | Higher power consumption due to active components. | Lower power consumption, leading to better energy efficiency. |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance to clean and replace fans or other active components. | Minimal maintenance with fewer parts susceptible to wear and tear. |
| Durability | Moving parts may fail over time, reducing overall durability. | More durable due to lack of moving parts; ideal for harsh environments. |
| Initial Cost | Can be more expensive due to the need for additional cooling components. | Generally less expensive with fewer components required. |
| Application Suitability | Suitable for gaming, high-performance computing, and environments where performance is prioritized. | Ideal for industrial settings, offices, and applications where noise reduction and reliability are critical. |
| Heat Dissipation | Actively dissipates heat away from the system quickly. | Relies on natural heat dissipation, which may be slower. |
Industrial Applications of Fanless Computers
Fanless computers are becoming increasingly valuable in various industrial applications due to their durability, reliability, and silent operation. Let’s explore some of the key areas where these systems are making a significant impact.

Automation and Control Systems
Fanless computers are integral to modern manufacturing lines and automation processes. Their ability to operate reliably in harsh environments with dust, vibrations, and extreme temperatures makes them ideal for controlling machinery, monitoring production lines, and ensuring seamless operations.
Surveillance and Security
The reliability and silent operation of fanless computers make them perfect for surveillance and security applications. They are often used in security cameras, monitoring systems, and other surveillance equipment, where their lack of noise and need for minimal maintenance are significant advantages.
Data Acquisition
Fanless computers are crucial in data acquisition tasks, where they collect and process data from various sensors and devices in real-time. Their robust design allows them to function efficiently in challenging industrial environments, ensuring accurate and continuous data flow.
Transportation and Logistics
In the transportation and logistics sector, fanless computers are used in vehicles and other transportation systems for monitoring and control purposes. Their ability to withstand vibrations and temperature variations makes them suitable for use in trucks, trains, and other transport vehicles, where they help in tracking, navigation, and system management.
Limitations and Considerations
While fanless computers offer many advantages, there are some challenges and factors to consider before making the switch. Understanding these can help you determine if a fanless system is the right fit for your industrial needs.
Potential Limitations
- Performance: Fanless computers generally have lower performance capabilities compared to fan-cooled systems. They may struggle with high-end computing tasks like advanced gaming or intensive graphic design.
- Heat Management: While effective, passive cooling might not be sufficient for the most demanding applications, potentially leading to thermal throttling under heavy loads.
Considerations for Selecting the Right Fanless Computer
- Environmental Conditions: Ensure the computer can withstand specific environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and temperature extremes.
- Workload Requirements: Match the computer’s capabilities with the workload demands of your application. For instance, less intensive tasks may suit fanless systems better.
- Space Constraints: Consider the physical space available for installation. Fanless computers are often more compact, which can be a crucial factor in tight spaces.
- Maintenance and Longevity: Evaluate the long-term maintenance needs and lifespan expectations, as fanless systems generally require less maintenance and have a longer lifespan.
By understanding these challenges and considerations, you can make an informed decision about whether a fanless computer is the right choice for your industrial application.
Exploring Geniatech’s Solutions
Among various leading solutions that employ fanless technology, Geniatech’s Commercial Tablet and Mini Industrial PC stand out.
Geniatech Commercial Tablet: This rugged, industrial-grade tablet is perfect for demanding environments. Its fanless design ensures silent operation, reduced maintenance, and increased durability. Ideal for commercial and industrial use, it combines robust performance with energy efficiency.
Geniatech Mini Industrial PC: These compact, fanless embedded box PCs excel in industrial applications. Designed for harsh conditions, they provide robust performance and reliability without the noise and mechanical failure risks associated with traditional cooling systems. The ARM-based architecture enhances power efficiency, making them suitable for continuous operation in challenging settings.
Why Choose Geniatech?
Geniatech is committed to innovation and quality, ensuring the products meet and exceed industry standards. Both the Commercial Tablet and Mini Industrial PC showcase the advantages of fanless technology, offering superior performance, low power consumption, and longevity.
Conclusion
Fanless computers offer silent operation, durability, low maintenance, and energy efficiency, making them ideal for industrial applications such as automation, surveillance, data acquisition, and transportation. While they may not match the performance of fan-cooled systems for high-end tasks, their reliability in harsh environments is unmatched. Consider fanless computers to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs in your industrial setup, ensuring continuous and dependable performance.

