Single Board Computers
What is a Single Board Computer?
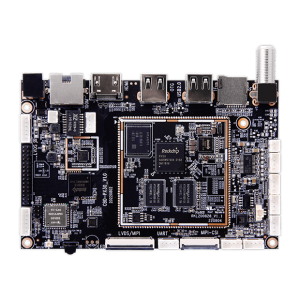
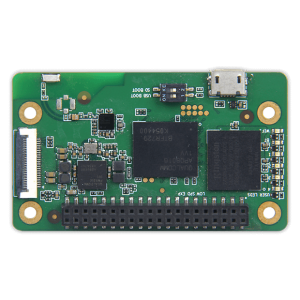
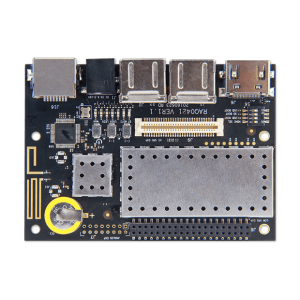
Single board computers (SBCs) are complete computer systems where all major components (such as CPU, memory, storage, network interfaces, etc.) are integrated into a single small-sized board. These computers are typically used in embedded systems, education, prototyping, and entertainment projects. SBCs offer functionalities similar to desktop or laptop computers but are typically smaller, cheaper, and have lower power consumption. If you’re interested, click here to learn more about embedded computers and how they work.
PLC vs SBC
PLCs are specialized computers primarily used in industrial settings for controlling machinery and processes, featuring rugged design and tailored programming languages like ladder logic. embedded board, on the other hand, are versatile computing platforms employed in diverse applications, offering flexibility in programming languages and capabilities beyond industrial control. Understanding how to choose the Single Board Computer for your projects can significantly impact their efficiency and functionality
While PLCs excel at real-time control in industrial environments, ARM SBCs offer greater flexibility, computing power, and versatility, making them suitable for a wider range of applications beyond traditional industrial control.
Single board computer industrial applications
- Industrial Automation and Control: industrial SBCs are used for controlling and monitoring manufacturing processes, machinery, and equipment in industrial automation systems. They can execute control algorithms, interface with sensors and actuators, and communicate with other devices in real-time.
- Data Acquisition and Logging: embedded SBCs are employed to collect data from sensors, instruments, and devices distributed across industrial environments. They can log data, perform data preprocessing, and transmit information to central databases or cloud platforms for analysis and decision-making.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: SBCs computer enable remote monitoring and control of industrial processes and equipment. They can be integrated with communication modules (such as Ethernet, Wi-Fi, or cellular) to facilitate remote access and control from centralized control centers or mobile devices.
- Edge Computing: AI SBCs enable edge computing architectures, processing and analyzing data closer to its source to reduce latency and bandwidth usage. Capable of executing edge analytics algorithms, filtering data, and providing real-time insights, they empower efficient decision-making at the network’s edge.
- Prototyping and Development: small SBCs are valuable tools for prototyping new industrial automation systems, testing control algorithms, and developing custom solutions. They enable rapid prototyping and iterative development of industrial applications before deployment at scale.